Monetary policy
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) has various statutory tasks. Which one of the tasks listed below is among them?
What annual change in Switzerland’s price level (i.e. inflation) is consistent with the SNB’s definition of price stability?
Which of the following statements are correct and which are not? Please briefly explain your answer.
Is a temporarily negative inflation rate a problem? Please answer in three to four complete sentences.
Imagine a scenario in which prices are threatening to rise (i.e. there is a risk of inflation). The SNB therefore decides to adjust the policy rate.
Please indicate whether the SNB will increase or lower its policy rate and what effect this adjustment will have on the other economic factors (rise, decrease).


The transmission mechanism (cf. knowledge sheet on monetary policy, diagram 1) describes the effect a monetary policy decision has on the economy. Please explain in four to five sentences what this means in the case of Switzerland. Take into consideration that Switzerland, as a small economy geared to the global markets, is heavily influenced by international economic developments.
The following statements refer to the transmission mechanism (cf. knowledge sheet on monetary policy, diagram 1). Which are correct and which are not? Please briefly explain your answer.
The statements below describe the monetary policy decision-making process. However, they are not listed in the correct sequence.
Arrange the statements in the correct sequence by entering the letters A to E in the field to the left of each statement.
| If the forecast points to a breach of price stability over the next few quarters (on the assumption that the policy rate remains unchanged), monetary policy action is required. | |
| As a last step, the monetary policy decision is announced in a press release. Moreover, the central bank’s management explains the decision at a news conference twice a year. | |
| The central bank’s management meets regularly for a monetary policy assessment. The most important tool in the decision-making process is the analysis of economic data. | |
| On this basis, the central bank reaches a monetary policy decision: What monetary policy would be appropriate from the present standpoint? Does the current monetary policy need to be adjusted? | |
| As a first step, the central bank analyses the overall economic situation over the past few quarters as well as the forecasts for the current and the coming quarters. |
There is always a degree of uncertainty involved in a central bank’s decision. Please explain in three to four sentences what this statement means and how this influences the central bank’s decision-making process.
Fill in the gaps in the text below with the appropriate words.
challenge / negative interest rates / times of crisis / overvaluation / minimum exchange rate / zero
Political stability, a solid fiscal and monetary policy and the resulting robust economy make the Swiss franc a perfect safe-haven currency: In , Swiss investors flock back to the Swiss franc, while international investors seek it out for security reasons. This safe-haven role of the Swiss franc represents a for Switzerland’s economy as the franc tends to appreciate whenever a global crisis looms. This pattern was particularly pronounced in the years following the financial crisis (2007 to 2009). The resulting of the Swiss franc and the associated deflationary pressure led the SNB to intervene in the foreign exchange market and to introduce a of CHF 1.20 per euro for a limited period of time (from September 2011 to January 2015), as no other measures were available due to interest rates being close to percent. Finally, at the end of 2014, were introduced, too, which lasted as long as September 2022.
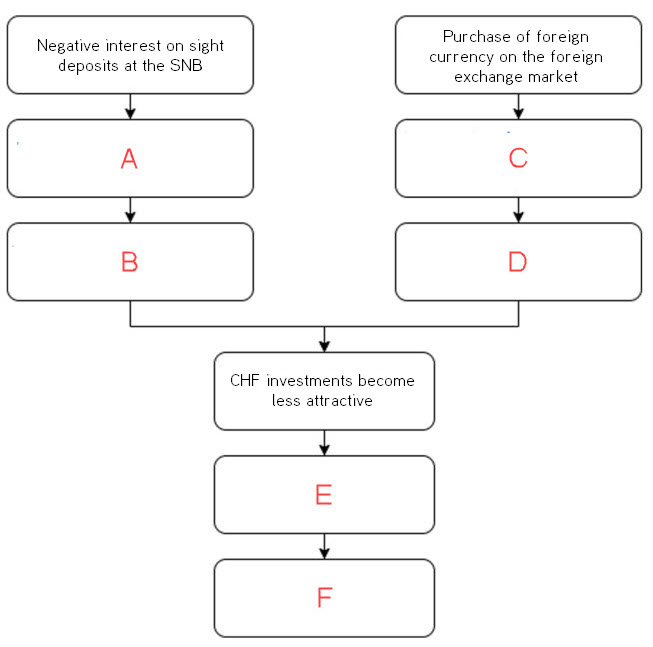
| Value of Swiss franc decreases, value of foreign currency increases | |
| Upward pressure on Swiss franc decreases | |
| Low or negative interest rates in Switzerland | |
| Lower demand for Swiss francs | |
| Banks pass on negative interest rates | |
| Additional supply of Swiss francs, additional demand for foreign currency |
Please explain in three to four sentences why the SNB cannot indefinitely lower interest rates into negative territory.
Which unconventional monetary policy measures were taken outside Switzerland, e.g. in the US or in the euro area? Please give at least two examples. Use the internet to do some research.
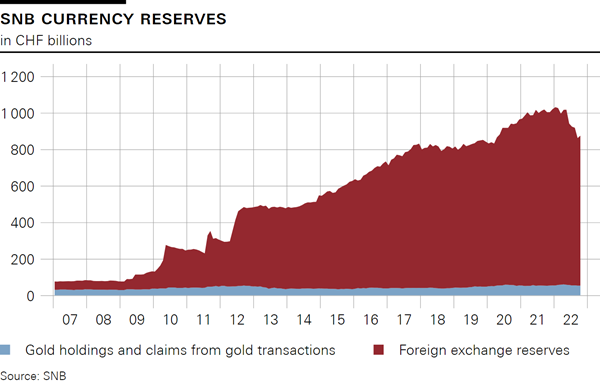
Development of the SNB’s currency reserves, broken down into gold holdings and claims from gold transactions as well as foreign exchange reserves.