Economic trends, summer 2022
Every quarter, the Federal Government’s Expert Group publishes a
The summer forecast was presented on 15 June 2022 with a SECO press release and documented in a comprehensive SECO publication entitled ‘Konjunkturtendenzen’/‘Tendances conjoncturelles’ (see illustration opposite).
This publication is freely accessible online in German or French at www.seco.admin.ch/Konjunkturtendenzen.
In this task, Iconomix presents a concise summary on the basis of excerpts from the 25-page publication and the press release from SECO. It then sets a number of questions on the SECO text. Questions marked with the ✪ icon are advanced questions that go beyond the excerpts from the text and encourage further thought.
The summary is structured as follows: As a small economy geared to the global markets, Switzerland is heavily influenced by international economic developments. For this reason, the summary starts with an outline of the global economic situation and the monetary environment. The second section looks into the economic situation in Switzerland in the past quarter, while the third presents the latest economic forecast. The fourth part of the summary explains the risks to economic developments and the forecast.

Slide set with charts and tables
The Iconomix unit ‘Economic trends’ also includes a PDF slide set containing all the charts and tables from the corresponding SECO publication, covering areas such as contributions made by the various economic sectors to GDP growth, global trade and inflation trends.
Real economy
The prospects for the international economy have waned. World market prices have risen sharply for key Russian and Ukrainian exports, such as energy resources and certain food staples and animal feeds The resulting inflationary pressure is curbing demand in major trading partners, with adverse effects on exposed sectors of the Swiss economy. At the same time, China’s drastic pandemic containment measures are likely to weigh heavily on its economy.
Monetary developments
Inflation rates, already high, have risen again in the last three months (see illustration below) and in many places have reached their highest level since the beginning of the 1980s. This is largely due to the sustained upward trend in commodity prices. Following the Bank of England, the UK’s central bank, the US central bank has now also raised its key interest rate, known as the federal funds rate, twice in recent months. Expansionary monetary policy has been retained so far in the euro area. The European Central Bank, however, has announced an initial increase in interest rates for July.
Since the beginning of the year there has been a widespread decline in the stock markets. On the other hand, higher inflation expectations have led to an increase in long-term interest rates.
Illustration from SECO’s ‘Konjunkturtendenzen’/‘Tendances conjoncturelles’ publication:
Inflation in selected countries
Percentage changes compared to the same month one year earlier
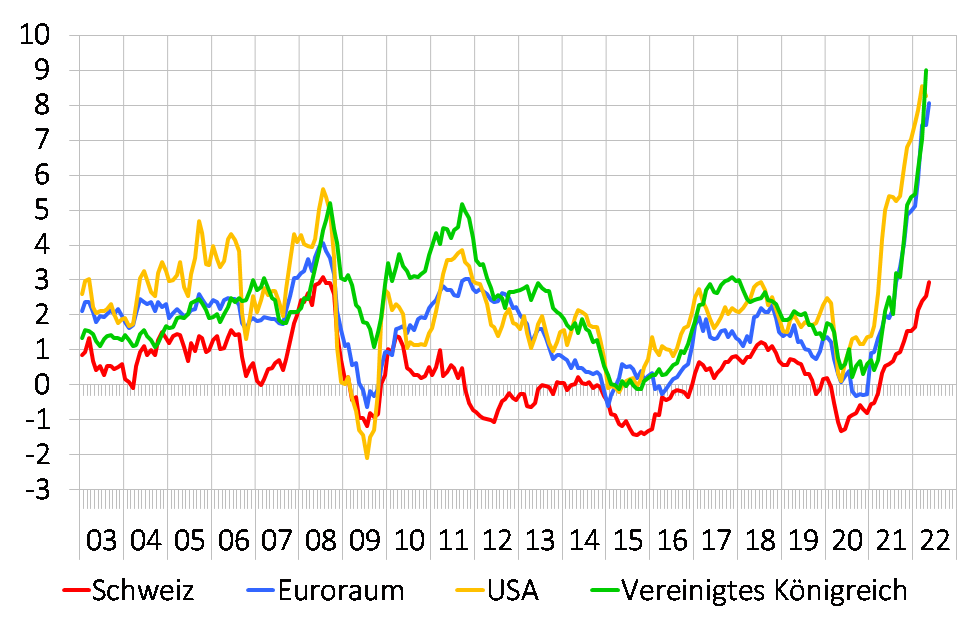
Sources: BFS, Eurostat, U.S. BLS, ONS
Questions on the international and monetary environment
Describe the current global economic situation.
How would you describe monetary developments?
In recent months, inflation has risen strongly all over the world. What have been the biggest factors driving prices up?
✪ In the text it says that the inflationary pressure resulting from increasing prices is curbing demand. What is meant by this? Answer in two to three sentences.
✪ In the text it says that, as well as the Bank of England, the US central bank has now also raised its key interest rate. Describe what a central bank intends to do when it increases its key interest rate.
Gross domestic product
The Swiss economy continued to recover during the first quarter, as expected. GDP adjusted for sporting events grew 0.4%, which is in line with the historical average. The manufacturing sector in particular contributed to the continuing economic recovery. Parts of the service sector, by contrast, were still being held back at the beginning of the year by the most recent wave of coronavirus and the accompanying measures.
The economic indicators currently point to a continued recovery, albeit less dynamic than could have been expected at the beginning of the year.
Labour market
In mid-March 2020 the coronavirus pandemic hit the labour market abruptly. A good two years on and it has largely recovered.
Prices
Inflation continued its most recent upward trend, reaching 2.9% in May. Similarly high figures were last recorded in 2008. Unlike the situation at that time, however, around half of the current inflation is due to higher energy prices. So far, inflationary developments in Switzerland have been moderate compared with other countries.
Questions on the economic situation in Switzerland
How did the Swiss economy develop in the first quarter of 2022? What do the signals point to for the second quarter?
What was the situation on the labour market?
How did inflation develop?
✪ The economic impact of the war in Ukraine on Switzerland has so far been limited. Give reasons for this in two or three sentences.
✪ An appreciation of the Swiss franc is leading to slower price growth in Switzerland. Give reasons for this in one or two sentences.
GDP and prices
The Swiss economy made a solid start to the year, but prospects for the international environment have waned. Against this backdrop, the expert group has lowered its 2022 growth forecast for Switzerland to 2.6% (GDP adjusted for sporting events; forecast from March: 2.8%).
It has also revised its inflation forecast for Switzerland to 2.5% (forecast from March 2022: 1.9%) and is assuming a negative knock-on effect on private consumer spending.
Increased uncertainty, supply bottlenecks and rising prices are deterring investment activity. For the time being, therefore, the Swiss economy looks set to continue its recovery from the pandemic with above-average GDP growth, but at a slower pace than projected in the previous forecast. This is assuming no significant downturn in important trading partners and, in particular, no pronounced energy or commodity shortages in Europe.
In the second half of the forecast period, the catch-up effect in relation to the pandemic is likely to fade. The economy is expected to normalise, provided that the current limiting factors gradually ease, especially the global supply chain problems and high international inflation. The tightening of monetary policy worldwide is likely to have a dampening effect. For 2023 as a whole, the expert group has lowered its GDP growth forecast to 1.9% (adjusted for sporting events; forecast from March: 2.0%). Inflation is predicted to fall to an average of 1.4% for the year (forecast from March: 0.7%).
Labour market
For the labour market, the expert group anticipates further recovery and is forecasting an average unemployment rate of 2.1% in 2022, followed by 2.0% in 2023.
Questions on the economic forecast
What GDP growth is the Federal Government’s Expert Group expecting for 2022 and 2023?
What rate of unemployment is expected for the forecast period?
How will inflation develop over the forecast period?
On what assumption is the comparatively favourable forecast based? Answer in one or two sentences.
✪ Prices have also risen across the board in Switzerland, albeit not as sharply as in other currency areas. Have you already noticed price increases in your everyday life? How are you responding to them?
War in Ukraine
Uncertainty in connection with the Ukraine conflict is very high. Even without international military escalation, there is a risk that the economic impact will be greater than assumed in the current forecast.
The Swiss economy would be hard hit if major trading partners were to see a significant economic downturn, for example as the result of widespread shortfalls in energy supplies from Russia. Such a scenario would be likely to lead to great pressure on prices both in Switzerland and other European countries, accompanied by a decline in economic growth.
Rising interest rates
Rising interest rates are exacerbating the risks related to a sharp rise in debt internationally. There is an increased likelihood of corrections on the financial markets. Risks also remain in the real estate sector, both in Switzerland and internationally.
Coronavirus crisis
Finally, setbacks in the pandemic, for example resulting from new variants, cannot be ruled out. In particular there is a risk that further highly restrictive coronavirus measures in China could adversely affect the international economy.
Questions on the risks
Uncertainty is currently very high, and the forecast is subject to risks primarily on the downside. Describe the main downside risks in your own words.
How would the Swiss economy be affected by a scenario where all Russian energy and commodity deliveries to the EU were blocked? Answer in key words.
✪ Inflation forecasts are currently subject to a great deal of uncertainty. A lot depends on whether the increase in prices will be reinforced by a so-called wage-price spiral. What is meant by this?